Home
Welcome to Precise Force Field and Bioinformatics Laboratory
Precise Force Field and Bioinformatics Laboratory was established by Professor Hai-Feng Chen in January of 2007, belonged to State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism. Our lab is focused on the methodology of computational biology and bioinformatics to insight into the molecular mechanism of complex diseases. The representative works are developed the precise force field of the intrinsically disordered proteins. We developed a set of new force fields based on AMBER, CHARMM, and OPLS, such as ff99IDPs, ff14IDPs, ff14IDPSFF, ff03CMAP, ESFF1, CHARMM36IDPSFF, and OPLSIDPSFF. Many peers including computational biologist of Andrew McCammon and Ken A. Dill used these force fields or wrote the review to introduce them.
Academic News
2020 paper accepted:
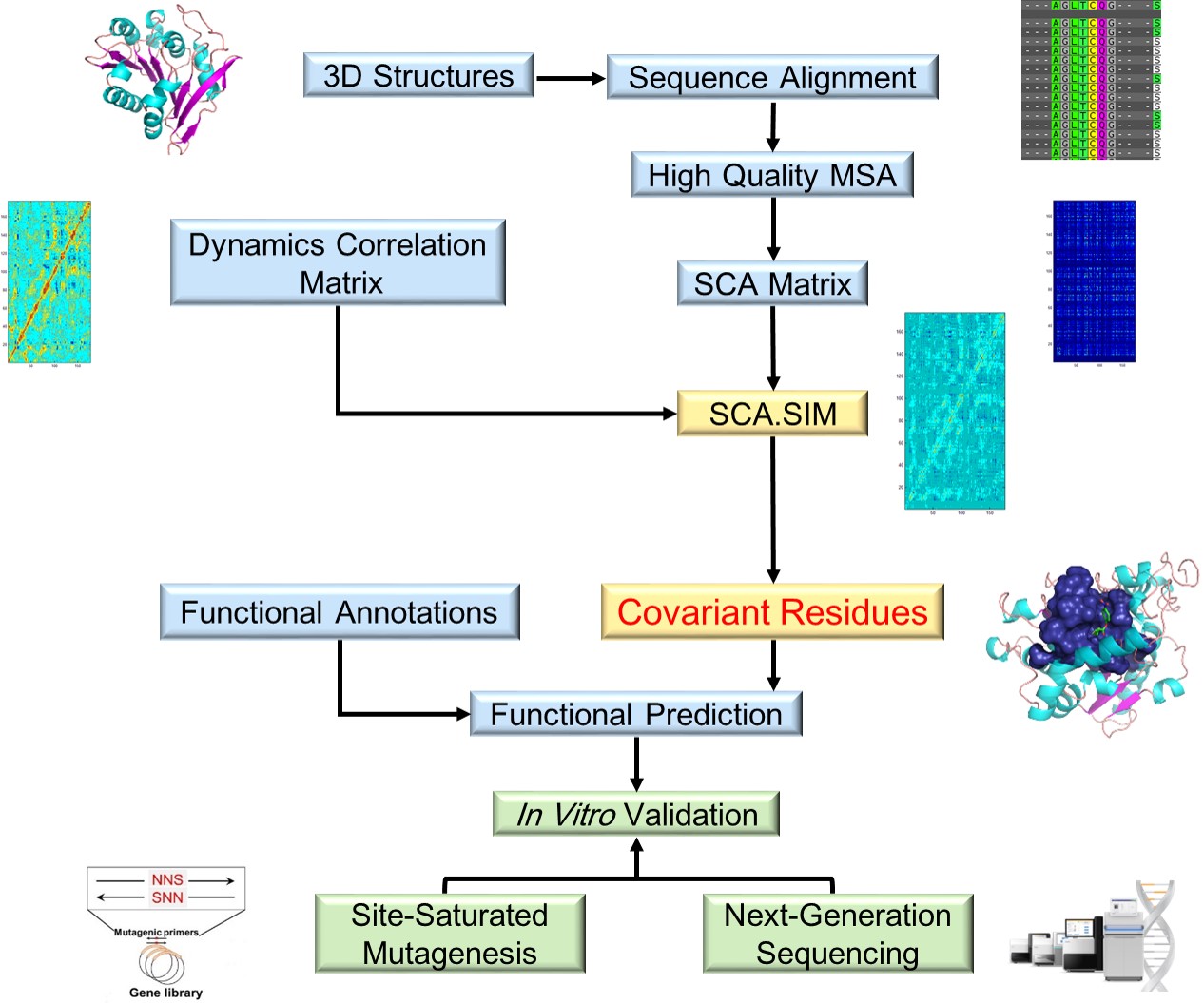
The paper titled "Algorithm-based Coevolution Network Identification Reveals Key Functional Sectors of the α/β Hydrolase Subfamilies" has been accepted by The FASEB Journal. (doi)
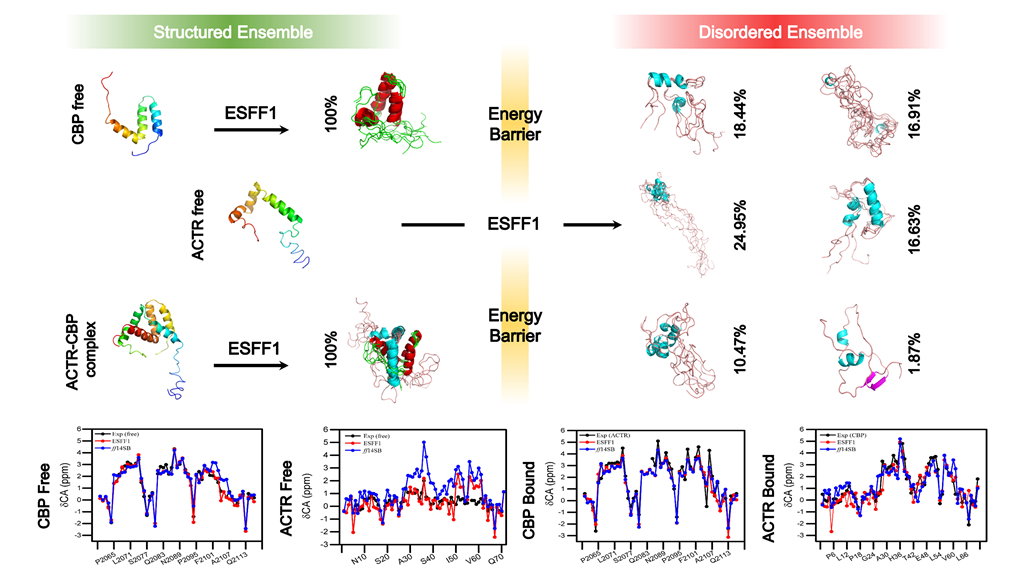
The paper titled "Environment-Specific Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered and Ordered Proteins" has been accepted by J. Chem. Inf. Model. (doi) Reported on WeChat Official Accounts
2019 paper accepted:
The paper titled "Well-balanced Force Field ff03CMAP for Folded and Disordered Proteins" has been accepted by J. Chem. Theory Comput. (doi)
The paper titled " Dynamical Important Residue Network (DIRN): Network Inference via Conformational Change" has been accepted by Bioinformatics. (doi) Reported on Academic News of SJTU
2018 paper accepted:
The paper titled "Order-Disorder Transition of Intrinsically Disordered Kinase Inducible Transactivation Domain of CREB" has been accepted by J. Chem. Phys.. (doi)
Research
1. Precise Force field of intrinsically disordered proteins
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) are not fixed three dimension structure under physiological conditions. These IDPs comprise a large portion of eukaryotic proteomes (between 35% and 51%) which were found to link with Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, amyloidosis, diabetes, and others diseases. As the diverse flexible conformers of IDPs, it is very challenging to experimentally characterize a conformational ensemble with X-ray, NMR or cryo-EM. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations can sample continuous conformers that might provide a valuable complement to experimental data. Nevertheless the MD simulation community still faces two major limitations: sampling adequacy and force field accuracy.
In order to solve these problems, we developed a set of precise force fields of ff99IDPs, ff14IDPs, ff14IDPSFF, ff03CMAP, ESFF1, CHARMM36IDPSFF, and OPLSIDPSFF to improve the sampling of IDPs. The relative papers are published on the Journal of Chem. Biol. Drug & Des. (2014, 2017, 2018), J. Chem. Inf. Model. (2015, 2017, 2019, 2020), and J. Chem. Theory Comput. (2019). After we published the work, we received a set of emails from the peer to request the force field parameters, such as, Andrew McCammon group from University of California (San Diego) and University of Nebraska from USA, Imperial College London of UK, Jülich Research Centre and University of Osnabrück from Germany, University of Nice and University of Marseille from France, Curtin University of Australia, University of Ioannina from Greece, Indian institute of technology and University of Calcutta from India, and so on. Professor Ken A Dill (National Academy of Sciences) from Stony Brook University comments that ff99IDPs force field improves the agreement with experiment (Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 36:25–31, 2016).

2. Computer Aided Innovation Drug Design
Computer aided innovation drug design uses AI method to build molecular modeling and investigate the interaction between drug and receptor, then optimize and design the lead compound. In our lad, we used 3D-QSAR model combined with molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation to research HIV-1 protease, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, HIV-1 integrase, CCR5, antitumor, and COVID-19, and build robust prediction models. China Economic Herald and CludAI Time reported the virtual screening of anti-COVID-19 inhibitors..

3. Protein Design
Protein design includes rational design, semirational design, and directed evolution. We used AI method to train a new SCA model, named SCA.SIM, (website is under construction now) by integrating structure information and MD simulation data to predict the key function site of enzyme..
Team
Principal Investigator

Professor Dr. Hai-feng Chen
PhD supervisor Precise Force Field and Bioinformatics Laboratory Department of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology Room 512, Building 3 of Comprehensive Experimental Building 800 Dongchuan Road, Minhang District Shanghai, 200240, China E-mail:haifengchen@sjtu.edu.cn
PostDocs

Ashfaq Ur Rehman
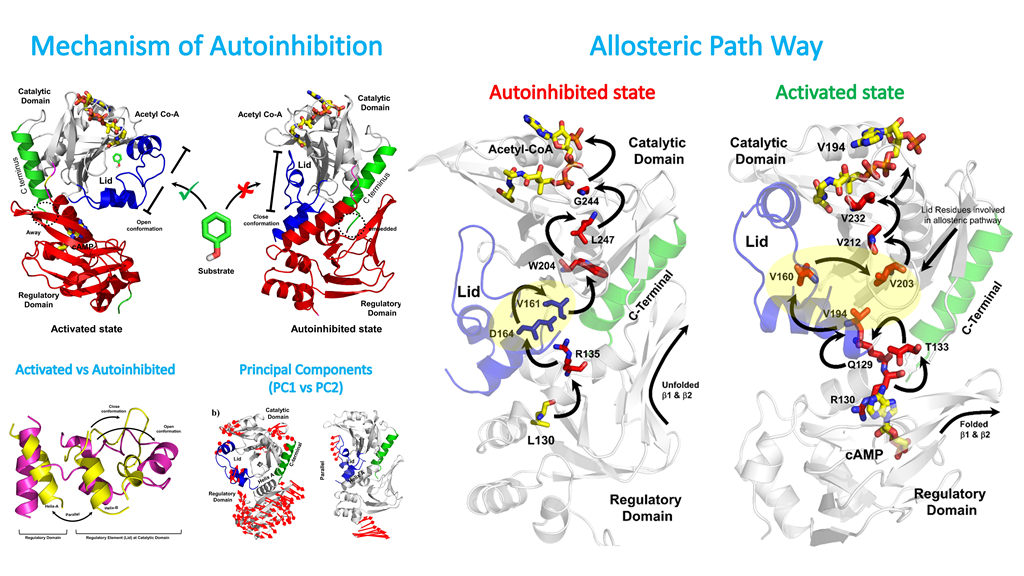
Join time: 2016.9 Background: Biochemistry Research Direction: Allosteric Regulation Mechanism of Autoinhibited proteins Email: raysjtu@sjtu.edu.cn
Students

Hao Liu
Join time: 2014.9 (Phd candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of IDP force field Email: haoliu_sjtu@foxmail.com

Xiaochen cui
Join time: 2019.9 (Phd candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of IDP force field Email: cxc_cc@sjtu.edu.cn

Taaha
Join time: 2018.9 (Phd candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Email:

Xiaoyue Ji
Join time: 2020.9 (Phd candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of IDP force field Email: xy15037859990@163.com

Xiaopian Tian
Join time: 2018.9 (Master candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of PTM force field Email: tianxp18@sjtu.edu.cn

Jun Chen
Join time: 2019.9 (Master candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of RNA force field Email: 0706cj@sjtu.edu.cn

Yuxin Jiang
Join time: 2020.9 (Master candidate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Email:

Bozitao Zhong
Join time: 2017.9 (Undergraduate) Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and test of PTM force field Email: zbztzhz@163.com

Zhengsong Pan
Join time: Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Email:

Tiantian Cheng
Join time: Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Email:

Kairan Zhang
Join time: Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Email:
Previous Students

Yue Chen
Join time: 2008.9 Background: Biotechnology Research Direction: Molecular dynamic simulation, drug design Email: chenyuewillsh@icloud.com

Wei Ye
Join time: 2010.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Development and application of molecular force field, data analysis of multi-omics Email: yangjingxusjtu@163.com

Jingxu Yang
Join time: 2011.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Molecular dynamic simulation, analysis of allosteric pathway and network Email: yangjingxusjtu@163.com

Cheng Jiang
Join time: 2012.9 Background: Biotechnology Research Direction: Riboswitch, molecular regulation Email: jiang_cheng1990@163.com

Jinmai Zhang
Join time: 2013.9 Background: Biochemistry and molecular biology Research Direction: Molecular dynamic simulation, genome analysis, gene editing Email: zhangjinami@sjtu.edu.cn

Lishi Xu
Join time: 2013.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Molecular dynamic simulation, enzyme evolution Email: laplacecat@hotmail.com

Tianle Qian
Join time: 2015.7 Background: Structural Biology Research Direction: Molecular dynamic simulation, structure and function of protein Email: qiantianle8881@163.com

Xiang Guo
Join time: 2015.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Force field test, folding mechanism of c-Myb Email: df1992@sjtu.edu.cn

Quan Li
Join time: 2016.6 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Molecular dynamics simulation, research of protein allosteric mechanism, network analysis Email: leejack@sjtu.edu.cn

Dong Song
Join time: 2016.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Force field development, computer aid drug design Email: dongsong@sjtu.edu.cn

Aohuan Dan
Join time: 2017.8 Background: Biochemical Engineering Research Direction: Force field test, molecular dynamic simulation of IDP Email: danaohuan@sjtu.edu.cn

Yangpeng Zhang
Join time: 2017.9 Background: Bioinformatics Research Direction: Force field development Email: zhangyp@sjtu.edu.cn
Go to topLiterature
Representative Publications
1. Z. Wu, H. Liu, L. Xu, H.F. Chen*, Y. Feng*. Algorithm-based Coevolution Network Identification Reveals Key Functional Sectors of the α/β Hydrolase Subfamilies. The FASEB Journal. 2020, 34:1983-1995. (IF=5.391)
2. D. Song, H. Liu, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Environment-Specific Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered and Ordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60:2257−2267.
3. Y. Zhang, H. Liu, S. Yang, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Well-balanced Force Field ff03CMAP for Folded and Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019,15:6769-6780. (IF=5.313) (Citation: 1)
4. Q. Li, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Dynamical Important Residue Network (DIRN): Network Inference via Conformational Change. Bioinformatics. 2019, 35:4664-4670.
5. D. Song, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. The IDP-Specific Force Field ff14IDPSFF Improves the Conformer Sampling of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57:1166-1178 (Citation: 48).
6. J. Yang, H. Liu, X. Liu, C. Gu, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Synergistic Allosteric Mechanism of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and Serine for Pyruvate Kinase M2 via Dynamics Fluctuation Network Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56: 1184-1192 (Citation: 19).
7. W. Ye, D. Ji, W. Wang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Test and Evaluation of ff99IDPs Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55: 1021-1029 (Citation: 34).
8. W. Wang, W. Ye, C. Jiang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. New force field on modeling intrinsically disordered proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84: 253-269 (citation: 56).
9. Z. Huang, L. Zhu, Y. Cao, G. Wu, X. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Wang, T. Shi, Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, W. Li, Y. Li, H.F. Chen*, G. Chen, J. Zhang*. ASD: a comprehensive database of allosteric proteins and modulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39: D663-D669 (Citation: 97).
10. F. Qin, Y. Chen, M. Wu, Y. X. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Induced Fit or Conformational Selection for RNA/U1A folding. RNA. 2010, 16:1053-1061 (Citation: 40).
11. H.F. Chen*. Mechanism of Coupled Folding and Binding in the siRNA-PAZ Complex. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4: 1360-1368 (Citation: 34).
12. H.F. Chen, R. Luo*. Binding induced folding in p53-MDM2 complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129:2930-2937 (Citation: 92).
All Publications
1. Y. Zhang, H. Liu, S. Yang, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Well-balanced Force Field ff03CMAP for Folded and Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15:6769-6780. (IF=5.313) (Citation: 1)
2. Q. Li, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Dynamical Important Residue Network (DIRN): Network Inference via Conformational Change. Bioinformatics. 2019, 35:4664-4670.
3. Z. Wu, H. Liu, L. Xu, H.F. Chen*, Y. Feng*. Algorithm-based Coevolution Network Identification Reveals Key Functional Sectors of the α/β Hydrolase Subfamilies. The FASEB Journal. 2020, 34:1983-1995. (IF=5.391)
4. D. Song, H. Liu, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Environment-Specific Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered and Ordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60:2257−2267.
5. A. Rehman, M, Rahman, S. Lu, H. Liu, J.Y. Li, T. Arshad, A. Wadood, H. L. Ng, H.F. Chen*. Decoding Allosteric Communication Pathways in Protein Lysine Acetyltransferase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2020, 147:70-80.
6. A. Ur Rehman, H. Rafiq, M. Ur Rahman, J. Li, H. Liu, S. Luo, T. Arshad, A. Wadood, H.F. Chen*. Gain-of-Function SHP2 E76Q Mutant Recusing Autoinhibition Mechanism Associated with Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59:3229-3239.
7. A. Ur Rehman, M. T. Khan, H. Liu, A. Wadood, S. I. Malik, H.F. Chen*. Exploring the Pyrazinamide Drug Resistance Mechanism of Clinical Mutants T370P and W403G in Ribosomal Protein S1 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59: 1584-1597.
8. S. Yang, H. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. Lu*, H.F. Chen*. Residue-Specific Force Field Improving the Sample of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Folded Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59:4793-4805.
9. H. Liu, D. Song, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Extensive Test and Evaluation of CHARMM36IDPSFF Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered Protein and Folded Protein. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21:21918-21931.
10. Y. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Allosteric Mechanism of an Oximino-piperidino-piperidine Antagonist for the CCR5 Chemokine Receptor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 95:113-123.
11. A. Dan, H.F. Chen*. Secondary structures transition of tau protein with intrinsically disordered proteins specific force field. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93:242–253.
12. A. Ur Rehman, M. Ur Rahman, M. T. Khan, S. Saud, H. Liu, D. Song, P. Sultana, A. Wadood, H.F. Chen*. The Landscape of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (Shp2) and Cancer. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2018, 24: 3767-3777.
13. H. Liu, X. Guo, J. Han, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Order-Disorder Transition of Intrinsically Disordered Kinase Inducible Transactivation Domain of CREB. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2018, 148:225101.
14. W. Fan, H. Liu, P. Liu, X. Deng, H. F. Chen, Q. Liu, Y. Feng. Characterization of protein interaction surface on fatty acyl selectivity of starter condensation domain in lipopeptide biosynthesis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2020, 104: 653–660.
15. Y. Tan, Y. Zhang, Y. Han, H. Liu, H.F. Chen, F. Ma, S. G. Withers, Y. Feng, G. Yang*. Directed evolution of an α1,3-fucosyltransferase using a single-cell ultrahigh-throughput screening method. Science Advances. 2019, 5:eaaw8451.
16. Z. Yang, B. Xu, X. Hu, X. Yao, Y. Tang, C. Qian, S. Wang, H.F. Chen, X. Bai, J. Wu*. Dynein axonemal intermediate chain 2 plays a role in gametogenesis by activation of Stat3. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23:417-425.
17. L. Zhou, M. Li, X.Y. Wang, H. Liu, S. Sun, H.F.Chen, A. Poplawsky, Y.W. He*. Biosynthesis of Coenzyme Q in the Phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris via a Yeast-Like Pathway. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32:217-226.
18. H.X. Jiang, J. Wang, L. Zhou, Z.J. Jin, X.Q. Cao, H. Liu, H.F. Chen, Y.W. He*. Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in the biopesticide Shenqinmycin-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain M18. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology. 2019, 46:1025–1038.
19. L. Feng, C. Chang, D. Song, C. Jiang, Y. Song, C. Wang, W. Deng, Y. Zou, H.F. Chen, X. Xiao, F. Wang, X. Liu*. The trimeric Hef-associated nuclease HAN is a 3’→5’ exonuclease and is probably involved in DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Research. 2018, 46:9027-9043.
20. Y. J. Ye, L. Zhou, X. Liu, H. Liu, D. Li, M. Cao, H.F. Chen, L. Xu, J. Zhu, Y. Zhao*. A novel chemical inhibitor of ABA signaling targets all ABA receptors. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173:2356-2369. (Citation: 0).
21. Q. Li, H.F. Chen*. Synergistic regulation mechanism of iperoxo and LY2119620 for muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor. RSC Advances. 2018, 8:13067-13074.
22. H. Liu, D. Song, H. Lu*, R. Luo*, H.F. Chen*. Intrinsically Disordered Protein Specific Force Field CHARMM36IDPSFF. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 92:1722-1735. (Cover image + Editor’s choice)
23. D. Song, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. The IDP-Specific Force Field ff14IDPSFF Improves the Conformer Sampling of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57:1166-1178 (Citation: 2).
24. 9. W. Ye, T. Qian, H. Liu, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Allosteric Autoinhibition Pathway in Transcription Factor ERG: Dynamics Network and Mutant Experimental Evaluations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57:1153-1165 (Citation: 1).
25. 10. Y. Cai, H. Liu, H.F. Chen. Allosteric mechanism of quinoline inhibitors for HIV RT-associated RNase with MD simulation and dynamics fluctuation network. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, in press.
26. 11. X. Guo, J. Han, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Conformation Dynamics of Intrinsically Disordered Protein c-Myb with ff99IDPs Force Field. RSC Advances. 2017, 7:29713 –29721 (Citation: 0).
27. PoH. Liu, W. Ye, H.F. Chen*. Positive Cooperative Regulation of Double Binding Sites for Human Acetylcholinesterase. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89:694-704 (Citation: 0).
28. D. Song, W. Wang, W. Ye, D. Ji, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. ff14IDPs Force Field Improving the Conformation Sampling of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89:5-15 (Citation: 2).
29. T. Qian, J. Wo, Y. Zhang, Q. Song, G. Feng, R. Luo, S. Lin, G. Wu, H.F. Chen*. Crystal Structure of StnA for the Biosynthesis of Antitumor Drug Streptonigrin Reveals a Unique Substrate Binding Mode. Scientific Reports. 2017, 7:40254 (Citation: 0).
30. J. Zhang, C. Jiang, W. Ye, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Allosteric Pathways in Tetrahydrofolate Sensing Riboswitch with Dynamics Correlation Network. Mol. BioSyst. 2017, 13:156 -164 (Citation: 0).
31. Y. J. Ye, L. Zhou, X. Liu, H. Liu, D. Li, M. Cao, H.F. Chen, L. Xu, J. Zhu, Y. Zhao*. A novel chemical inhibitor of ABA signaling targets all ABA receptors. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173:2356-2369. (Citation: 0).
32. M. A. Hoque, Y. Zhang, L. Chen, G. Yang, M. A. Khatun, H.F. Chen, L. Hao, Y. Feng*. Stepwise Loop Insertion Strategy for Active Site Remodeling to Generate Novel Enzyme Functions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12:1188–1193. (Citation: 0).
33. X. Lv, H. Liu, H.F. Chen, H. Gong*. Coupling between ATP hydrolysis and protein conformational change in maltose transporter. Proteins. 2017, 85:207-220 (Citation: 0).
34. J. Zhang, H. Luo, H. Liu, W. Ye, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Synergistic Modification Induced Specific Recognition between Histone and TRIM24 via Fluctuation Correlation Network Analysis. Scientific Reports. 2016, 6: 24587 (Citation: 7).
35. W. Wang, C. Jiang, J. Zhang, W. Ye, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Dynamics Correlation Network for Allosteric Switching of PreQ1 Riboswitch. Scientific Reports. 2016, 6: 31005 (Citation: 1).
36. J. Yang, H. Liu, X. Liu, C. Gu, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Synergistic Allosteric Mechanism of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and Serine for Pyruvate Kinase M2 via Dynamics Fluctuation Network Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56: 1184-1192 (Citation: 7).
37. M. Rahman, H. Liu, A. Wadood, H.F. Chen*. Allosteric Mechanism of Cyclopropylindolobenzazepine Inhibitors for HCV NS5B Rdrp via Dynamics Correlation Network Analysis. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12:3280-3293 (Citation: 0).
38. W. Ye, D. Ji, W. Wang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Test and Evaluation of ff99IDPs Force Field for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55: 1021-1029 (Citation: 15).
39. D. Ji, W. Ye, H.F. Chen*. Revealing the binding mode between respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein and benzimidazolebased inhibitors. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11: 1857-1866 (Citation: 0).
40. L. Xu, W. Ye, C. Jiang, J. Yang, J. Zhang, Y. Feng, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Recognition Mechanism between Lac Repressor and DNA with Correlation Network Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2015, 119: 2844-2856 (Citation: 2.
41. K. Wu, J. Pang, D. Song, Y. Zhu, C. Wu, T. Shao, H.F. Chen*. Selectivity Mechanism of ATP-Competitive Inhibitors for PKB and PKA. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86:9-18. (Citation: 1).
42. W. Wang, W. Ye, C. Jiang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. New force field on modeling intrinsically disordered proteins. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84: 253-269 (citation: 28).
43. Q. Yu, W. Ye, C. Jiang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Specific Recognition Mechanism between RNA and KH3 Domain of Nova-2 Protein. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2014, 118: 12426-12434. (Citation: 1).
44. Q. Yu, W. Ye, W. Wang, H.F. Chen*. Global Conformational Selection and Local Induced Fit for the Recognition between Intrinsic Disordered p53 and CBP. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8:e59627 (Citation: 5).
45. W. Wang, W. Ye, Q. Yu, C. Jiang, J. Zhang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Conformational Selection and Induced Fit in Specific Antibody and Antigen Recognition: SPE7 as a Case Study. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2013, 117:4912-4923 (Citation: 7).
46. W. Ye, J. Yang, Q. Yu, W. Wang, J. Hancy,R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Kink Turn sRNA Folding upon L7Ae Binding with Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15:18510-18522 (Citation: 8).
47. S. Ma, W. Ye, D. Ji, H.F. Chen*. Insight into the Binding Mode between HIV-1 Integrase and Pyrimidone Analogue Inhibitors with MD Simulation and 3D-QSAR. Med. Chem. 2013, 9:420-433 (Citation: 0).
48. W. Ye, F. Qin, J. Zhang, R. Luo, H.F. Chen*. Atomistic Mechanism of microRNA Translation Upregulation via Molecular Dynamics Simulations. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7: e43788 (Citation: 7).
49. W. Ye, Y. Chen, W. Wang, Q. Yu, Y. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Insight into the Stability of cross-beta Amyloid Fibril from VEALYL Short Peptide with Molecular Dynamics Simulation. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7: e36382 (Citation: 5).
50. F. Qin, W. Ye, Y. Chen, X. Chen, Y. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Specific Recognition between Intrinsically Disordered LEF and DNA. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14: 538-545 (Citation: 13).
51. G. Yan, Y. Chen, Y. Li, H.F. Chen*. Revealing Interaction Mode between HIV-1 Protease and Mannitol Analog Inhibitor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79:916-925 (Citation: 0).
52. Z. Huang, L. Zhu, Y. Cao, G. Wu, X. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Wang, T. Shi, Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, W. Li, Y. Li, H.F. Chen*, G. Chen*, J. Zhang*. ASD: a comprehensive database of allosteric proteins and modulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39: D663-D669 (Citation: 66).
53. F. Qin, Y. Jiang, Y. Chen, M. Wu, G. Yan, W. Ye, Y. X. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Conformational Selection or Induced Fit for Brinker and DNA Recognition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13:1407-1412 (Citation: 18).
54. H. Zhang, F. Qin, W. Ye, Z. Li, S. Ma, Y. Xia, Y. Jiang, J. Zhu, Y. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Revealing the Drug-Resistant Mechanism for Diarylpyrimidine Analogue Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2011, 78:427-437 (Citation: 5).
55. J. Xiong, H. Wang, G. Guo, S. Wang, L. He, H.F. Chen*, J. Wu. Male Germ Cell Apoptosis and Epigenetic Histone Modification Induced by Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6: e20751 (Citation: 11).
56. Z. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Drug Resistant Mechanism of Diaryltriazine Analog Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation and 3D-QSAR. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2011, 77:63-74 (Citation: 4).
57. F. Qin, Y. Chen, M. Wu, Y. X. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Induced Fit or Conformational Selection for RNA/U1A folding. RNA. 2010, 16:1053-1061 (Citation: 32).
58. Y. Chen, Y.J. He, M. Wu, G. Yan, Y.X. Li, J. Zhang, H.F. Chen*. Insight into the Stability of Cross-β Amyloid Fibril from Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Biopolymers. 2010, 93: 578-586 (Citation: 19).
59. Y. Chen, Z. Li , H.F. Chen*. Computational Study of CCR5 Antagonist with Support Vector Machines and Three Dimensional Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship Methods. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2010, 75: 295-309 (Citation: 6).
60. H.F. Chen*. Aggregation Mechanism Investigation of the GIFQINS cross-Amyloid Fibril. Comput. Bio. Chem. 2009, 33: 41-45 (Citation: 18).
61. H.F. Chen*. In Silico logP Prediction for a Large Data Set with Support Vector Machines, Radial Basis Neural Networks and Multiple Linear Regression. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2009, 74: 142-147 (Citation: 6).
62. H.F. Chen*. Post-translational Modification of Phosphorylated KID from Molecular Dynamics Simulation. PLoS ONE. 2009, 4: e6516 (Citation: 37).
63. F. Qin, Y. Chen, Y. X. Li, H.F. Chen*. Induced Fit of mRNA/TIS11d Complex. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131: 115103 (Citation: 23).
64. H.F. Chen*. Mechanism of Coupled Folding and Binding in the siRNA-PAZ Complex. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4: 1360-1368 (Citation: 29).
65. H.F. Chen*. Quantitative predictions of gas chromatography retention indexes with support vector machines, radial basis neural networks and multiple linear regression. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 609:24-36 (Citation: 26).
66. H.F. Chen*. Computational study of histamine H3-receptor antagonist with support vector machines and three dimension quantitative structure activity relationship methods. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 624:203-209 (Citation: 10).
67. H.F. Chen*. Computational Study of the Binding Mode of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Kinase Inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2008, 71:434-446 (Citation: 12).
68. Z. Li, J. Han, H.F. Chen*. Revealing Interaction Mode between HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase and Diaryltriazine Analog Inhibitor. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2008, 72:350-359 (Citation: 8).
69. H.F. Chen*, M.Y. Wu, Z. Wang, D.Q. Wei. Insight into the Metabolism Rate of Quinone Analogues from Molecular Dynamics Simulation and 3D-QSMR Methods. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2007, 70:290-301 (Citation: 4).
70. H.F. Chen, R. Luo*. Binding induced folding in p53-MDM2 complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129:2930-2937 (Citation: 80).
71. Z. Wang, J. Zhang, H. Li, J. Li, M. Niimi, G. Ding, H.F. Chen, J. Xu, H. Zhang, Z. Xu, Y. Dai, T. Gui, S. Li, Z. Liu, S. Wu, M. Cao, L. Zhou, X. Lu, J. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Fu, D. Yang, J. Song, T. Zhu, S. Li, B. Ning, Z. Wang, T. Koike, M. Shiomi, E. Liu, L. Chen, J. Fan, Y. E. Chen, Y. Li*. Hyperlipidemia-associated gene variations and expression patterns revealed by whole-genome and transcriptome sequencing of rabbit models. Scientific Reports. 2016, 6:26942 (Citation: 0).
72. L. Dong, Q. Tan, W. Ye, D. Liu, H.F. Chen, H. Hu, D. Wen,Y. Liu, Y. Cao, J. Kang, J. Fan, W. Guo, W. Wu*. Screening and Identifying a Novel ssDNA Aptamer against Alphafetoprotein Using CE-SELEX. Scientific Reports. 2015, 5:15552 (Citation: 5).
73. Y. Zhang,J. An,G.Y. Yang,A. Bai,B. Zheng,Z. Lou,G. Wu,W. Ye,H.F. Chen, Y. Feng*, G. Manco. Active Site Loop Conformation Regulates Promiscuous Activity in a Lactonase from Geobacillus kaustophilus HTA426. PLos ONE. 2015, 10:e0115130 (Citation: 2 ).
74. J. Gao,X. Luo*,Y. Li,R. Gao,H.F. Chen, D. Ji. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 2-oxo-pyrazine-3-carboxamide-yl Nucleoside Analogues and Their Epimers as Inhibitors of Influenza A Viruses. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2015, 85:245-252 (Citation: 2).
75. H. Zhang, Z. Liu, Y. Sun, J. Zhu, S. Lu, X. Liu, Q. Huang,Y. Xie, H. Zhu, S. Dang, H.F. Chen, G. Zheng, Y. Li, Y. Kuang, J. Fei, S. Chen, Z. Chen, Z.G. Wang*. Rig-I regulates NF-κB activity through binding to Nf-κb13′-UTR mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110:6459-6464 (Citation: 10).
76. H. Gu,H.F. Chen, D.Q. Wei, J.F. Wang*. Molecular dynamics simulations exploring drug resistance in HIV-1 proteases. Chinese Science Bulletin. 2010, 55:2677-2683 (Citation: 13).
77. J. Wang, C. Tan, H.F. Chen, R. Luo*. All-Atom Computer Simulations of Amyloid Fibrils Disaggregation. Biophys. J. 2008, 95:5037-5047 (Citation: 22).
78. C.F. Wang, H.Q. Zheng, H.C. Wei, R. Zhang, H.F. Chen, D.Q. Wei. Structure and vibrational frequencies of Ph3PCl2 with discrete solvent molecules and in gas phase. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 2007, 6:511-521 (Citation: 0).
79. T. Zhang, X. C. Dong, H.F. Chen, M. B. Chen. Docking Study on the Binding Modes of Sulfonylurea Analogues to ALS/AHAS and Virtual Screen of Novel Inhibitors. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2006, 64: 899-905. .
80. H.F. Chen, B.T. Fan*, C.Y. Zhao, L. Xie, C.H. Zhao, T. Zhou, K. H. Lee, G. Allaway. Computational Studies and Drug Design for HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors of 3’,4’-di-O-(S)-dicamphanoyl-(+)-cis-Khellactone (DCK) Analogs. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2005, 19:243-258 (Citation: 12)..
81. Q. Zhu, J. H.Yao, S. G. Yuan*, F. Li, H.F. Chen, W. Cai, Q. Liao. Superstructure Searching Algorithm for Generic Reaction Retrieval. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45:1214-1222.
82. C.Y. Zhao, G. Dodin, C.S. Yuan, H.F. Chen, R.L. Zheng, Z.J. Jia, B.T. Fan*. ‘In vitro’ protection of DNA from Fenton reaction by plant polyphenol verbascoside. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005, 1723:114-123 (Citation: 49).
83. B.T. Fan, H.F. Chen, H.R. Xia, M. Petitjean, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet*. New Strategy of Mass Spectrum Simulation Based on Reduced and Concentrated Knowledge Databases. Spectroscopy Lett. 2005, 38:145-170 (Citation: 8).
84. X.J. Yao, A. Panaye, J.P. Doucet, H.F. Chen, R.S. Zhang, B.T. Fan*, M.C. Liu, Z.D. Hu. Comparative classification study of toxicity mechanisms using support vector machines and radial basis function neural networks. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005, 535: 259-273 (Citation: 54).
85. X.J. Yao, A. Panaye, J.P. Doucet, R.S. Zhang, H.F. Chen, M.C. Liu, Z.D. Hu, B.T. Fan*. Comparative study of QSAR/QSPR correlations using support vector machines, radial basis function neural networks, and multiple linear regression. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2004, 44:1257-1266 (Citation: 148).
86. H.F. Chen, Q. Li, X.J. Yao, B.T. Fan*, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J.P. Doucet. CoMFA/CoMSIA/HQSAR and Docking Study of the Binding Mode of Selective Cyclooxygenase (COX-2) Inhibitors. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2004, 23:36-55 (Citation: 22).
87. H.F. Chen, X.J. Yao, M. Petitjean, H.R. Xia, J.H. Yao, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet, B.T. Fan*. Insight into the Bioactivity and Metabolism of Human Glucagon Receptor Antagonists from 3D-QSAR Analyses. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2004, 23:603-620 (Citation: 8).
88. H.F. Chen, J.H. Yao, J. Sun, Q. Li, F. Li, B.T. Fan, S.G. Yuan*. Discovery of anti-SARS Coronavirus Drug Based on Molecular Docking and Database Screening. Chinese Journal of Chemistry. 2004, 22:882-887..
89. Q. Zhu, J.H. Yao,F. Li, H.F. Chen, S.G. Yuan*. Comparison the similarity of R group. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2004, 62:1585-1589.
90. Q. Zhu, J.H. Yao,F. Li, H.F. Chen, S.G. Yuan*. The new method for the classification of reaction data and reaction knowledge. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2004, 62:112-119.
91. H.F. Chen, X.J. Yao, Q. Li, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet, B.T. Fan*. Comparative Study of Non Nucleoside Inhibitors with HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Based on 3D-QSAR and Docking. SAR and QSAR in Environ. Res. 2003, 14:455-474 (Citation: 24).
92. H.F. Chen, Q. Li, X.J. Yao, B.T. Fan*, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet. 3D-QSAR and Docking Study of the Binding Mode of Steroids to Progesterone Receptor in Active Site. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2003, 22:604-613 (Citation: 17).
93. H.F. Chen, X.C. Dong, B.S. Zeng, K. Gao, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet, B.T. Fan*. Virtual Screening and Rational Drug Design Method Using Structure Generation System Based on 3D-QSAR and Docking. SAR and QSAR in Environ. Res. 2003, 14:251-264 (Citation: 5).
94. H.F. Chen, B.T. Fan*, H.R. Xia, M. Petitjean, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet. MASSIS: A Mass Spectra Simulation System 1. Principal and Method. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 9:175-186 (Citation: 6).
95. H.F. Chen, B.T. Fan*, F. Li, M. Petitjean, H.R. Xia, S.G. Yuan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet. MASSIS: A Mass Spectra Simulation System 2. Procedures and Performance. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 9:445-457 (Citation: 3).
96. H.F. Chen, J.H. Kang, Q. Li, B. S. Zeng, X. J. Yao, B. T. Fan, S.G. Yuan*. A. Panaye, J.P. Doucet. 3D-QSAR Study on Apicidin Inhibit Histone Deacetylase. Chinese Journal of Chemistry. 2003, 21:1596-1607.
97. B.S. Hayat, H.F. Chen, S.G. Yuan, R. Wen*. 3D-QSAR Study on Diindolylmethane and Its Analogues with Comparative MolecularField Analysis (CoMFA). Chinese Journal of Chemistry. 2003, 21:20-24.
98. J.H. Kang, Y.T. Zhang, J. Chen, H.F. Chen, C. J. Lin, Q. Wang, Y.X. Ou*. Nickel-induced Histone Hypoacetylation: the Role of Reactive Oxygen Species. Toxicol Sci. 2003, 74:279-286.
99. H.F. Chen, K. Gao, B.T. Fan, S.G. Yuan*, Z.J. Jia, R.L. Zheng. A. Panaye, J.P. Doucet. Virtual Screening and Rational Design of Phenylpropanoid Glycosides Analogues Based on Molecular Docking. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2002, 60:1860-1866.
100. J.H. Yao, F. Li, S.W. Luo, S.G. Yuan, H.F. Chen, Q. Li, C.Z. Zheng. Automatic Identification of Tautomeric, Alternating and Aromatic Bonds in Chemical Structures. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2002, 60, 1291-1297.
101. H.F. Chen, Q. Li, B. S. Zeng, X.C. Dong, S.G. Yuan*, M.B. Chen, C.Z. Zheng, R.S. Sun, T.M. Cheng, Y.P. Shu, R.Q. Liu. 3D-QSAR Study on Anti-mast Cell Degranulation of Isoquinoline Compounds. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2001, 59:2143-2147.
102. H.F. Chen, X.C. Dong, Y. Gu, G.Q. Chai, S.X. Zhang, S.G. Yuan*, M.B. Chen, C.Z. Zheng. Study on Anti-Gibberella Fluorine-Containing Pesticides by 3D-QSAR. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:1074-1078.
103. Y. Gu, X.C. Dong, H.F. Chen, M.B. Chen*, S.X. Zhang, S.G. Yuan, C.Z. Zheng. 3D-QSAR Study of Flurine-Containing Pesticides. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:1540-1545.
104. Y. Gu, M.B. Chen*, X.C. Dong, H.F. Chen, B.S. Zeng, C.L. Feng, B.Yu, Y.Z. Hui. 3D-QSAR Studies of Saponins. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:1534-1539.
105. H.F. Chen, J.F. Li, J.H. Yao, S.G. Yuan*, C.Z. Zheng. Automatic Generation of Virtual Bio-Active Compounds. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:529-532.
106. H.F. Chen, Y. Gu, X.C. Dong, J.F. Li, S.X. Zhang, S.G. Yuan*, M.B. Chen, C.Z. Zheng. A New Method for De Novo Bio-Active Molecular Design. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:1168-1172.
107. H.F. Chen, S.G. Yuan*, S.W. Luo, X.C. Dong, J.H. Yao, S. Yang, C.Z. Zheng. Design of New HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors by Pharmacophore Searching. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2000, 58:287-292.
108. S.G. Yuan*, S.W. Luo, G.Q. Chai, J.H. Yao, H.F. Chen, C.Z. Zheng. From Pharmacophore to Leads: Bioactive Compound Discovery via Computer-aided Techniques. Chinese Journal of Chemistry. 1999, 17:237-243.
109. H.F. Chen, J.H. Yao, S.G. Yuan*, J. F. Li, S. Yang, C. Z. Zheng, B. T. Fan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet. Conformationally Flexible Searching in 3D Structure Searching System. Comput. & Appl. Chem. 1999, 16:101-104.
110. S.G. Yuan, J. H. Yao, H.F. Chen, C.Z. Zheng. Building up General Design of 3D Structure Searching System. Comput. & Appl. Chem. 1999, 15:77-80.
111. J.H. Yao, S.G. Yuan, H.F. Chen, C.Z. Zheng, S. Yang, B.T. Fan, A. Panaye, J. P. Doucet. Structure Indexing and Matching in 3D Structure Searching System. Comput. & Appl. Chem. 1999, 16:97-100.
112. S.G. Yuan, H.F. Chen, J. Xu, W.P. Xing, J.H. Yao, C.Z. Zheng. A New Definition of Molecular Similarity Based on Semantic Relation of 3D Structures. Comput. & Appl. Chem. 1999, 16:403-410.
Go to topDownload
Please fill the following information and select the software you want to download
Contact us
Precise Force Field and Bioinformatics Laboratory
State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism
Department of Bioinformatics & Biostatistics
School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Address: Room 512, Building 3 of Comprehensive Experimental Building, 800 Dongchuan Road, Minhang District, Shanghai, 200240, China
Tel:00862134204348
Fax:00862134204348
URL:http://cbb.sjtu.edu.cn/~hfchen/
E-mail:haifengchen@sjtu.edu.cn
Go to top